-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
Video
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message
Request a Quote

Livestock Injection plays a crucial role in maintaining animal health. It encompasses various techniques used to administer vaccines, medications, or nutrients to livestock. These injections ensure that animals receive proper care and can thrive in their environments.
Farmers rely on Livestock Injection to prevent diseases and manage health issues in herds. The introduction of vaccines through injection can drastically reduce the spread of infectious diseases. This proactive approach not only benefits the animals but also safeguards public health by ensuring safe food production.
However, challenges exist. Not all livestock may tolerate injections well. Sometimes, there are adverse reactions that can occur. Ensuring proper technique is essential for effectiveness. As we emphasize the importance of Livestock Injection, we must also reflect on the need for further education and training for those administering these injections. Improving methods can enhance the overall health of livestock populations.

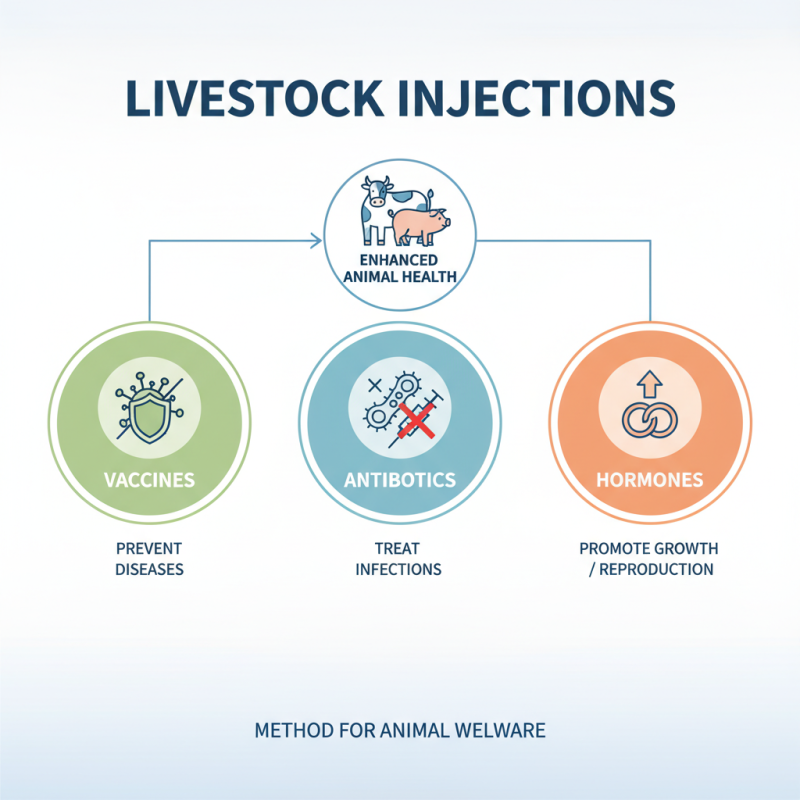
Livestock injection refers to the administration of substances to animals to enhance their health. This method includes vaccines, antibiotics, and hormones. Each type serves a unique purpose in maintaining animal welfare. Vaccines protect against diseases. Antibiotics treat infections. Hormones can promote growth or reproduction.
Understanding the types of injections is crucial for farmers. For example, subcutaneous injections go under the skin. Intramuscular injections enter the muscle. Each method has its technique and purpose.
Tips: Always use sterile needles. Proper injection techniques promote healing. Monitor animals after injections for any side effects. Ensuring correct dosage is vital. Mistakes can lead to health issues. These injections can sometimes leave marks or cause temporary discomfort. Consider observation important. Reflect on the animal's well-being regularly.
The practice of livestock injection has roots that date back centuries. Early veterinarians used crude instruments to deliver medicines. They often relied on simple techniques without a deep understanding of anatomy. As medicine progressed, so did animal treatment methods. Now, injections allow for precise dosages and faster absorption.
The importance of livestock injection lies in its impact on animal health. Vaccines and antibiotics are delivered efficiently, helping prevent diseases. This approach minimizes suffering in animals and reduces overall herd mortality. However, there were times when injections were misused, leading to complications. Improper techniques could cause stress or injury to the animal. These past mistakes remind us to remain vigilant in training and approach.
The evolution of techniques reveals much about veterinary medicine. From rudimentary methods, the field learned lessons in efficacy and safety. Today, ongoing research shapes best practices. Animal welfare should always guide these advancements. Yet, it's essential to remember that the journey is not perfect. Continuous reflection on methods is crucial for improvement.
Vaccination plays a crucial role in maintaining livestock health. Vaccines help protect animals from infectious diseases. According to the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE), vaccination can reduce disease prevalence by up to 70%. This statistic highlights the importance of immunization in livestock management.
In some regions, vaccination coverage remains alarmingly low. For instance, only 50% of livestock are vaccinated against common diseases in certain areas. This leaves many animals at risk. Farmers often cite cost concerns as a reason for low vaccination rates. However, the long-term benefits outweigh the initial expenses. Healthy livestock contribute to higher productivity and, ultimately, better profits.
The impact of vaccination extends beyond individual farms. Diseases can spread rapidly among livestock populations. An outbreak can devastate entire communities. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) notes that vaccination can help prevent economic losses in the livestock sector. Yet, access to vaccines and education about their importance is still limited in some regions. Continuous efforts are needed to improve vaccination rates and ensure the health of livestock worldwide.
Livestock injection is crucial for animal health. Proper techniques can greatly reduce the risk of infection. Following best practices ensures effective medication delivery. A study shows that improper injection methods can lead to abscesses in 20% of cases. This highlights the importance of training for handlers.
One fundamental practice is using sterile equipment. Needles should be single-use to prevent cross-contamination. A clean technique reduces the likelihood of disease transmission. According to the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE), nearly 40% of livestock diseases are preventable through proper vaccination strategies.
Location matters too. Injection sites should be chosen carefully. Administering injections in safe areas minimizes stress. If the site is incorrect, recovery can take longer. Injecting subcutaneously usually works well for vaccines. Intramuscular injections may be necessary for antibiotics but require more skill. Hands-on training can greatly improve proficiency.
The livestock injection technology landscape is rapidly changing. Innovations are aimed not only at improving animal health but also enhancing animal welfare. For instance, a recent industry report highlighted that about 70% of farmers are now adopting advanced injection techniques to ensure better efficacy and reduced stress during vaccination. By using less invasive methods, the stress levels in animals can diminish significantly.
However, as we witness progress, critical questions arise. Many farmers are concerned about the overall welfare implications of these technologies. Some reports suggest that while technology improves injection accuracy, it may inadvertently overlook individual animal comfort. For example, the relentless push for efficiency can lead to inadequate attention to each animal's unique needs. Balancing technological advancement with animal welfare requires ongoing reflection.
Future trends also indicate a shift towards automation in livestock injection. Drones and robotic systems promise to streamline the process. Yet, these innovations raise ethical considerations. How will farmers ensure personalized care when relying on machines? Industry data suggests that 60% of livestock producers are wary of becoming too dependent on automation. Finding the right balance between technology and compassionate care remains a crucial task for the agricultural community.