-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
Video
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message
Request a Quote

Livestock injection is a critical aspect of modern farming that significantly impacts animal health and productivity. According to a report by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), effective vaccination and medication practices enhance livestock immune responses. However, many farmers still need clarity on proper techniques. Missteps in livestock injection can lead to serious health issues, such as abscesses or infections.
Each year, improper injection practices account for approximately 10% of livestock-related health problems. This statistic emphasizes the importance of understanding various injection techniques. Farmers must be equipped with the right knowledge to ensure effective practices. For example, incorrect needle size or angle can affect drug absorption. Additionally, maintaining hygiene during injections is often overlooked, risking contamination and side effects.
Improving injection skills is not just beneficial for animal welfare; it can also enhance farm profitability. The National Animal Health Monitoring System (NAHMS) reports that well-managed livestock have better growth rates and lower veterinary costs. Yet, despite this, many farmers lack training or resources. Thus, learning the top livestock injection techniques is vital for every farmer seeking to optimize animal care and farm success.
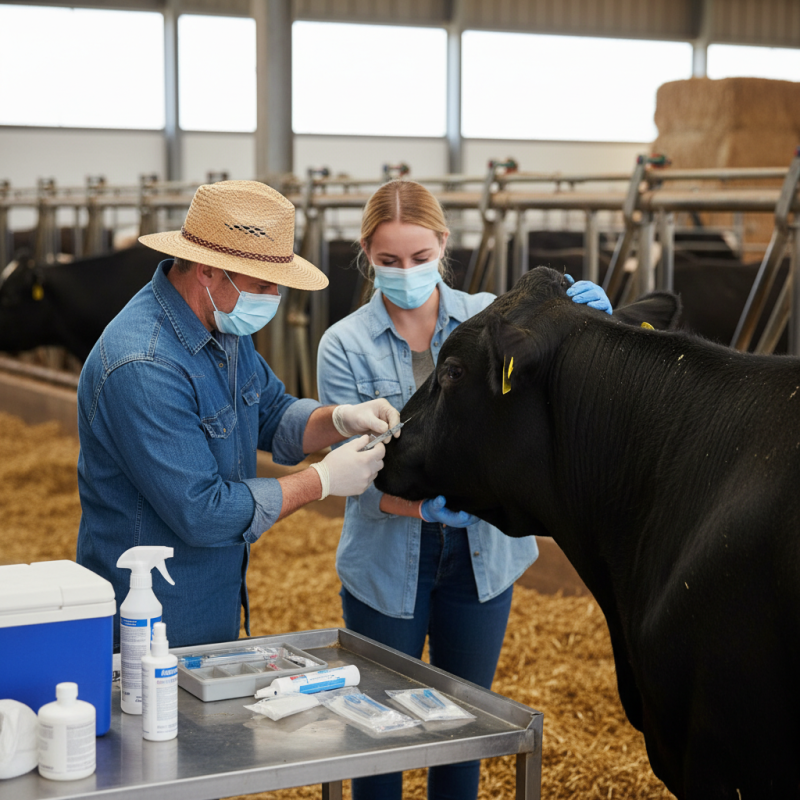

Livestock injection techniques are crucial for effective animal health management. Understanding these techniques can significantly impact herd productivity. A National Agricultural Statistics Service report indicates that improper injection methods can lead to inflammation, pain, and even reduced weight gain in livestock. Therefore, farmers should prioritize learning the most effective ways to administer injections.
The basics include understanding the three main routes: intramuscular, subcutaneous, and intravenous. Each route has its own specifics. For instance, injections delivered intramuscularly may yield faster absorption but could also carry risks like abscess formation if not done correctly. A 2021 study found that 30% of farmers overestimate their skills in executing these tasks, leading to frequent mistakes. Such errors can result in lost revenue and animal distress.
Farmers should also consider their equipment choices. Using clean and appropriate needles is critical. Research highlights that many farmers neglect needle length and gauge, contributing to complications. Inadequate training often results in inconsistent practices across farms, negating the potential benefits of vaccination programs. Each farmer needs to reflect on their injection techniques to improve animal welfare and overall farm efficiency.
Selecting the right injection site is crucial for effective medication delivery in livestock. The accuracy of your injection can impact the health and recovery of animals. According to a report by the World Organisation for Animal Health, improper injection techniques can lead to complications in 25% of livestock treated. Inadequate sites for injections can cause pain, inflammation, or even abscesses.
Common injection sites vary among species. For cattle, the neck is often preferred due to muscle mass and reduced risk of damaging vital organs. In pigs, the recommended site is the neck or behind the ear. Each region carries different risks. Misplacing an injection can compromise both efficacy and safety. Observations often reveal that many farmers still lack proper training in selecting injection points.
Farmers must remain aware of these factors. Experts suggest that practical training should be enhanced for more efficient procedures. Understanding animal anatomy is essential. This helps create a foundation for successful treatment. Many still overlook the potential for infection from repeated use of the same sites. Regular evaluation of injection practices is necessary.
Mastering livestock injection techniques is vital for effective animal health management.
Subcutaneous injections deliver vaccines or treatments just beneath the skin. This method is less painful and reduces stress for the animal.
Research by the American Veterinary Medical Association shows that proper subcutaneous techniques can improve absorption rates by up to 80%.
Intramuscular injections are used when a quick response is needed.
This technique involves injecting drugs directly into muscle tissues. It poses a higher risk of injury if not performed correctly.
Inadequate needle size can lead to tissue damage. The Purdue University Extension reports that incorrect positioning may result in ineffective treatment delivery in 15% of cases.
Farmers should continually reflect on their injection practices.
Training sessions can help improve their skills. Knowing when and how to use different injection sites is crucial.
Consider examining each injection's effectiveness regularly. This assessment can reveal areas that need improvement, ensuring overall herd health remains a top priority.

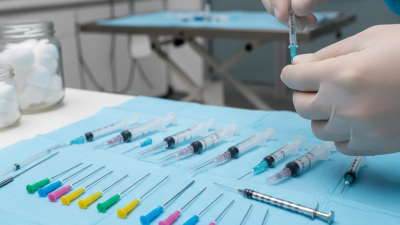
When handling livestock injections, safety protocols are crucial. Ensure the area is clean and organized. Gather all necessary tools before starting. This minimizes stress for both the animal and the farmer. Use a reliable restraint method to secure the animal. Improper handling can lead to injuries.
Proper injection techniques can prevent complications. Always use a clean needle for each injection. Needles can dull quickly, increasing discomfort. Change needles if they become bent or worn. Pay attention to the injection site. Choose appropriate muscles or skin areas to minimize pain.
Understanding animal behavior is essential. Animals can react unpredictably during procedures. Approach them calmly. Observe their movements and adjust your technique accordingly. Recording injection sites can help in future treatments. Reflect on each experience. Every farmer has room to improve their methods. Always strive for better outcomes and enhanced welfare for the animals.
Administering injections to livestock requires precision and care. Common mistakes can lead to stress and health issues. The wrong needle size is a frequent error. Using a needle that is too large can cause unnecessary pain. Conversely, a needle that is too small may not deliver the medication effectively.
Proper technique is crucial. Many farmers forget to ensure the cleanliness of the injection site. Infection risks increase when hygiene is compromised. Additionally, administering injections too quickly can result in complications. Research shows that slow administration allows for better absorption and reduces adverse reactions.
Overestimating the dosage can also be problematic. Studies indicate that nearly 15% of livestock farmers give incorrect doses. This not only jeopardizes animal health but can also lead to medication resistance. Farmers must be vigilant, check their measurements, and keep records updated. Reflecting on these practices can improve animal welfare and enhance overall farm productivity.