How Often Should You Drench Cattle for Best Results
Factors That Determine Drenching Frequency

Age and Immunity of Cattle
Younger cattle often have weaker immune systems, making them more vulnerable to parasites. Calves and yearlings typically require more frequent drenching to protect their health. As cattle age, their immunity improves, reducing the need for frequent treatments. However, stress or poor nutrition can weaken immunity, even in older animals. Regular health checks help you determine if your cattle need additional support.
Pasture Conditions and Parasite Risks
Parasites thrive in certain pasture conditions. Wet, muddy, or overgrazed areas create ideal environments for parasite eggs and larvae. If your cattle graze in these conditions, they face a higher risk of infection. Rotating pastures and maintaining clean grazing areas can reduce parasite exposure. You should also monitor the parasite load in your herd to decide when to use an animal drencher effectively.
Seasonal and Climatic Influences
Parasite activity often depends on the season and climate. Warm and humid weather promotes parasite growth, increasing the risk of infection. In contrast, colder months may slow parasite development. Understanding these patterns helps you plan drenching schedules. For example, you might need to drench more frequently during the rainy season when parasites are most active.
Herd Health and Management Practices
Healthy cattle are less likely to suffer from severe parasite infections. Providing balanced nutrition, clean water, and proper shelter strengthens their resistance. Good management practices, such as regular deworming and vaccination, also play a role. You should assess your herd's overall health and adjust drenching frequency based on their needs.
Best Practices for Using an Animal Drencher
Timing Drenching for Maximum Effectiveness
Timing plays a crucial role in achieving the best results from drenching. You should align treatments with the parasite life cycle to maximize effectiveness. For example, drenching before peak parasite activity, such as during the rainy season, helps reduce infestations. Avoid drenching too frequently, as this can lead to resistance. Instead, monitor your cattle’s health and use fecal egg counts to determine the right time for treatment.
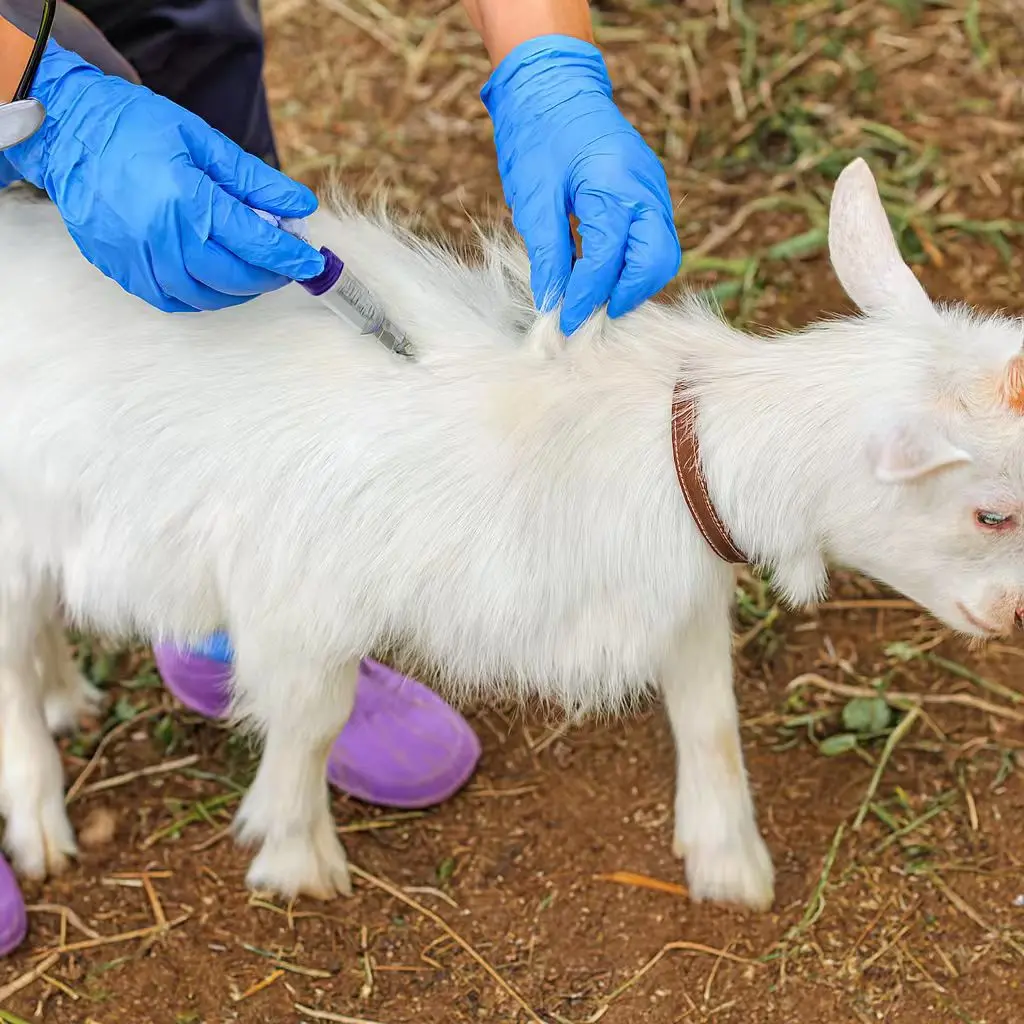
Selecting the Right Drenching Products
Choosing the correct drenching product ensures effective parasite control. Not all products target the same parasites, so you need to identify the specific threats in your herd. Consult a veterinarian or livestock expert to select the most suitable option. Always check the product label for dosage instructions and safety guidelines. Using the wrong product or incorrect dosage can harm your cattle and reduce the effectiveness of your animal drencher.
Proper Techniques for Administering Drenches
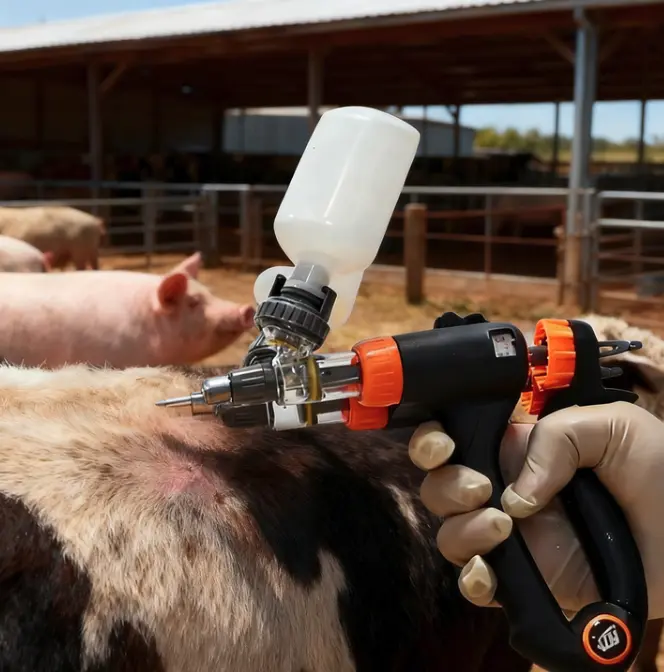
Administering drenches correctly ensures your cattle receive the full benefit of the treatment. Use a calibrated Drenching Gun to deliver the exact dosage. Insert the nozzle gently into the side of the mouth, aiming toward the back of the tongue. This method minimizes stress and ensures the drench is swallowed. Regularly clean and maintain your equipment to prevent contamination or malfunction.
Monitoring Results and Adjusting Strategies
After drenching, monitor your cattle for signs of improvement. Look for weight gain, healthier coats, and reduced parasite symptoms. Conduct follow-up fecal egg counts to measure the effectiveness of the treatment. If results are unsatisfactory, reassess your strategy. You may need to adjust the timing, switch products, or improve pasture management to achieve better outcomes.
Preventing Resistance to Drenches
Rotating Drenching Products
Rotating drenching products helps prevent parasites from developing resistance. Parasites adapt quickly when exposed to the same active ingredients repeatedly. You should alternate between products with different chemical groups to disrupt their life cycle. For example, if you use a macrocyclic lactone-based drench, switch to a benzimidazole-based one in the next treatment cycle. Always consult a veterinarian to choose the right rotation strategy for your herd.
Maintaining Refugia in the Herd
Maintaining refugia involves leaving a portion of the parasite population untreated. This practice ensures that non-resistant parasites remain in the environment, diluting the resistant ones. You can achieve this by not drenching a small group of healthy cattle with low parasite loads. These untreated animals help slow down resistance development. Regular monitoring ensures that this approach does not compromise herd health.
Avoiding Unnecessary Drenching
Unnecessary drenching wastes resources and accelerates resistance. You should only use an animal drencher when parasite levels pose a significant threat to your cattle. Conduct fecal egg counts to assess the parasite burden before deciding on treatment. Avoid routine drenching without evidence of need. This targeted approach protects your herd while preserving the effectiveness of drenching products.

Implementing Integrated Parasite Management (IPM)
Integrated Parasite Management (IPM) combines multiple strategies to control parasites effectively. You can use pasture rotation, nutritional support, and selective breeding alongside drenching. For instance, rotating pastures reduces parasite exposure, while providing balanced diets strengthens immunity. IPM reduces reliance on chemical treatments, making it a sustainable solution for long-term parasite control.
Effective drenching starts with understanding your cattle’s needs and the environment they live in. Use an animal drencher properly to ensure healthy, productive livestock.
Preventing resistance is essential. Follow best practices, monitor results, and adopt sustainable strategies. These steps protect your herd and maintain long-term parasite control. 🐄
FAQ
How do you know if your cattle need drenching?
Monitor for signs like weight loss, diarrhea, or poor coat condition. Conduct fecal egg counts to confirm parasite levels before deciding on treatment.
Can you drench cattle too often?
Yes, over-drenching can cause resistance in parasites. Use fecal egg counts and veterinary advice to determine the right frequency for your herd.
What is the best time of year to drench cattle?
Drench during peak parasite activity, often in warm, wet seasons. Adjust timing based on your region’s climate and pasture conditions.
---------------------------------------
To learn more please visit our website site_15eb649a-836b-4b55-827b-620be25f26cc
SHAOXING WANJIA APPLIANCE CO.,LTD.