How to Administer Chicken Vaccines Effectively: Tools, Techniques, and Best Practices
Vaccination is a vital part of poultry farming. Whether you're managing a small flock or running a large commercial operation, proper vaccine administration ensures flock immunity and reduces the risk of disease outbreaks. But more than just applying the vaccine, choosing the right veterinary instruments is key to effectiveness, animal welfare, and biosecurity.
In this guide, we’ll explore how to administer chicken vaccines using appropriate tools such as Automatic Syringes, dosing guns, and poultry vaccinators, while also covering best practices and key considerations.
Why Chicken Vaccination Matters
Chicken vaccines help prevent common infectious diseases like:
-
Newcastle Disease
-
Infectious Bronchitis
-
Marek’s Disease
-
Avian Influenza
-
Gumboro (IBD)
Without proper immunization, these diseases can wipe out entire flocks, impact productivity, and lead to significant economic losses.
Key Methods of Vaccine Administration in Poultry
1. Drinking Water Vaccination
Used for live vaccines (e.g., Newcastle, IBD). The vaccine is diluted into the flock’s drinking system.
Equipment used:
-
Medicator systems
-
Drinking water tubes
-
Water-soluble vaccine containers
Pro tips:
-
Ensure birds are thirsty (withdraw water 1–2 hours before).
-
Avoid chlorinated or iron-rich water.
2. Spray Vaccination
Ideal for respiratory vaccines like Infectious Bronchitis.
Equipment used:
-
Poultry vaccine sprayers
-
Atomizers or fine mist sprayers
Pro tips:
-
Use correct droplet size (coarse for older birds, fine mist for chicks).
-
Turn off ventilation during spraying for better absorption.
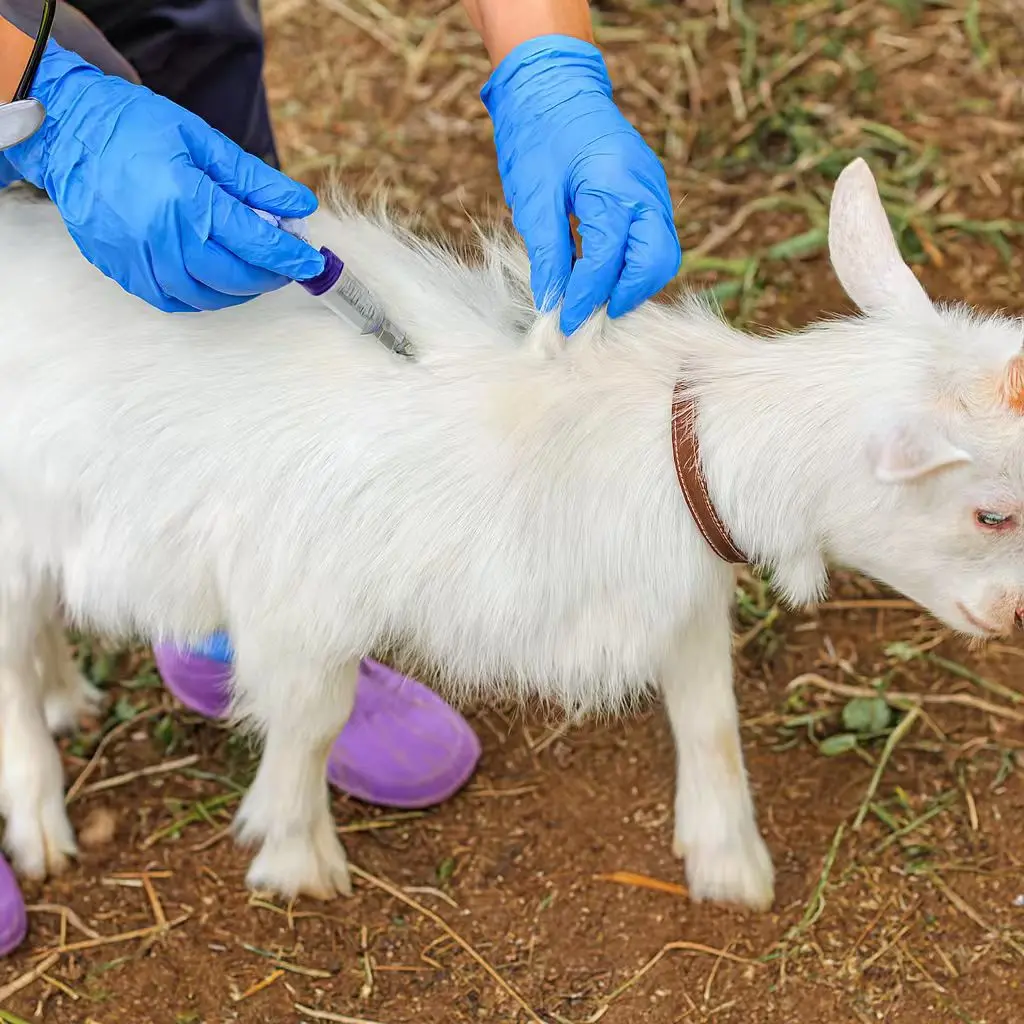
3. Injection Vaccination
Recommended for inactivated vaccines (e.g., Avian Influenza).
Tools required:
-
Automatic vaccination syringes (0.2ml to 1ml range)
-
Stainless steel needles or Plastic Syringes
-
Wing banding tools (for tracking vaccinated birds)
Best practices:
-
Subcutaneous injections (under the skin) for day-old chicks.
-
Intramuscular injections (thigh or breast) for older birds.
4. Eye Drop or Nasal Drop Vaccination
Common for Marek’s or Newcastle disease vaccines in chicks.
Tools used:
-
Precision droppers
-
Disposable pipettes
Technique tips:
-
Administer one drop per eye or nostril.
-
Confirm swallowing or blinking for proper dose uptake.
Choosing the Right Veterinary Equipment
As a veterinary device manufacturer, we recommend selecting:
-
Automatic poultry syringes – For fast and precise dosing
-
Multi-dose vaccinator guns – For high-volume operations
-
Dosing needles – Stainless steel or disposable plastic, depending on hygiene protocols
-
Vaccine mixing bottles – For safe and sterile vaccine preparation
High-quality tools reduce vaccine waste, improve efficiency, and minimize animal stress.
Additional Tips for Successful Poultry Vaccination
✅ Always follow the manufacturer's storage and handling guidelines.
✅ Use protective equipment and maintain hygienic procedures.
✅ Train staff to handle poultry gently and avoid injuries.
✅ Monitor birds after vaccination for any adverse reactions.
Conclusion
Proper vaccine administration in poultry isn’t just about the vaccine—it’s about using the right tools and techniques to ensure biosecurity, efficiency, and animal welfare. From automatic syringes to spray applicators, investing in reliable veterinary equipment helps maintain healthy flocks and protects your investment.
Looking for premium-quality poultry vaccinators, syringes, and veterinary instruments?
We are a 30-year OEM veterinary equipment manufacturer, offering export-grade tools trusted by clients worldwide.
👉 Contact us today to learn more or request a catalog.